We present a new type of map called iterable_big_map, which has the scalability property of a big_map, and which can be iterated like a basic map.
This feature was suggested by Nomadic Labs. Thank you to Lucas Feli and Charles Delhinger for the algorithm.
Example
Consider the following declaration of an iterable big map between a nat key and a bytes value:
variable ibm : iterable_big_map<nat, bytes> = []
While ibm has the scalability of a big map (in terms of number of entries), it can also be iterated with the for control instruction:
for (k,v) in ibm do
/* k is the key, v is the value */
done
An Archetype asset may now be compiled as an iterable big map; it then benefits from the whole asset API. For example:
asset car to iterable_big_map {
vin : string;
nbdoors : nat;
nbrepairs : nat;
owner : address;
}
Principle
Since it is always possible to iterate from 1 to n, the idea is to create a big map that associates the iteration integer value to the map's key value. It is also necessary to associate the map key back to this iteration integer (see remove operation below).
The following example illustrates the design of two big maps called Keys and Values derived from the original map:


- Keys associates the iteration integer with the map key
- Values is the original map where the value is augmented with the iteration integer
Add
The add operation consists in:
- associating the next iteration value (
Size + 1) with the new key in the Keys map - associating the new key to the pair of next iteration value and new value in the Values map
- incrementing the Size value
The operation is illustrated below with the addition of the key 131 with value e5:


Update
The update operation is straightforward and consists in updating the Values map with the new value.
Remove
The remove operation is a step-wise process:
- the iteration index of the removed key is retrieved from the Values map and used to remove the entry in the Keys map
- the entry is then removed from the Values map
At this stage, the iteration values are not consistent since one iteration value has been removed.
It is then necessary to associate the last added element with the removed iteration integer by:
- removing the last iteration integer and associate back the removed iteration integer with the last added key in the Keys mpa
- updating the iteration integer of last added key in the Values map
The process is illustrated below with the removal of the entry 29 (associated with iteration value 2):


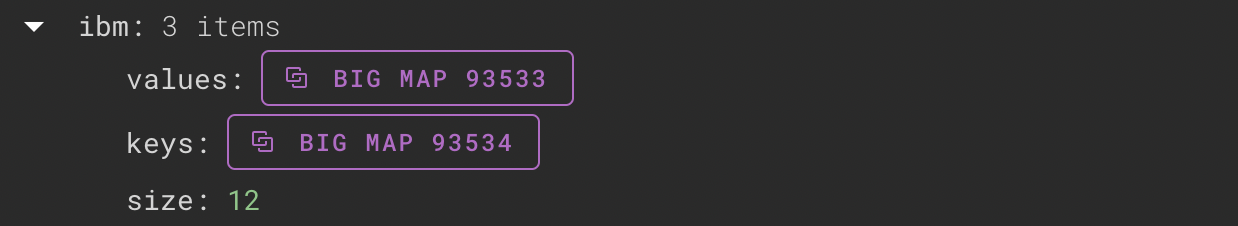
Implementation
An iterable big map is implemented as a triplet of two big maps (Keys and Values) and one Size integer.
The screenshot below of Better Call Dev shows the resulting triplet: